Biomedicines, Free Full-Text
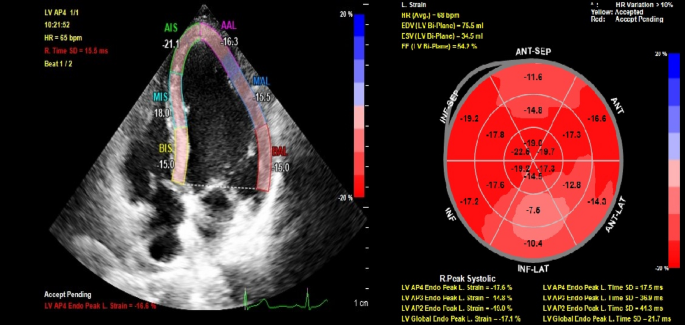
Left ventricular mechanics in Behcet's disease: A speckle tracking echocardiographic study
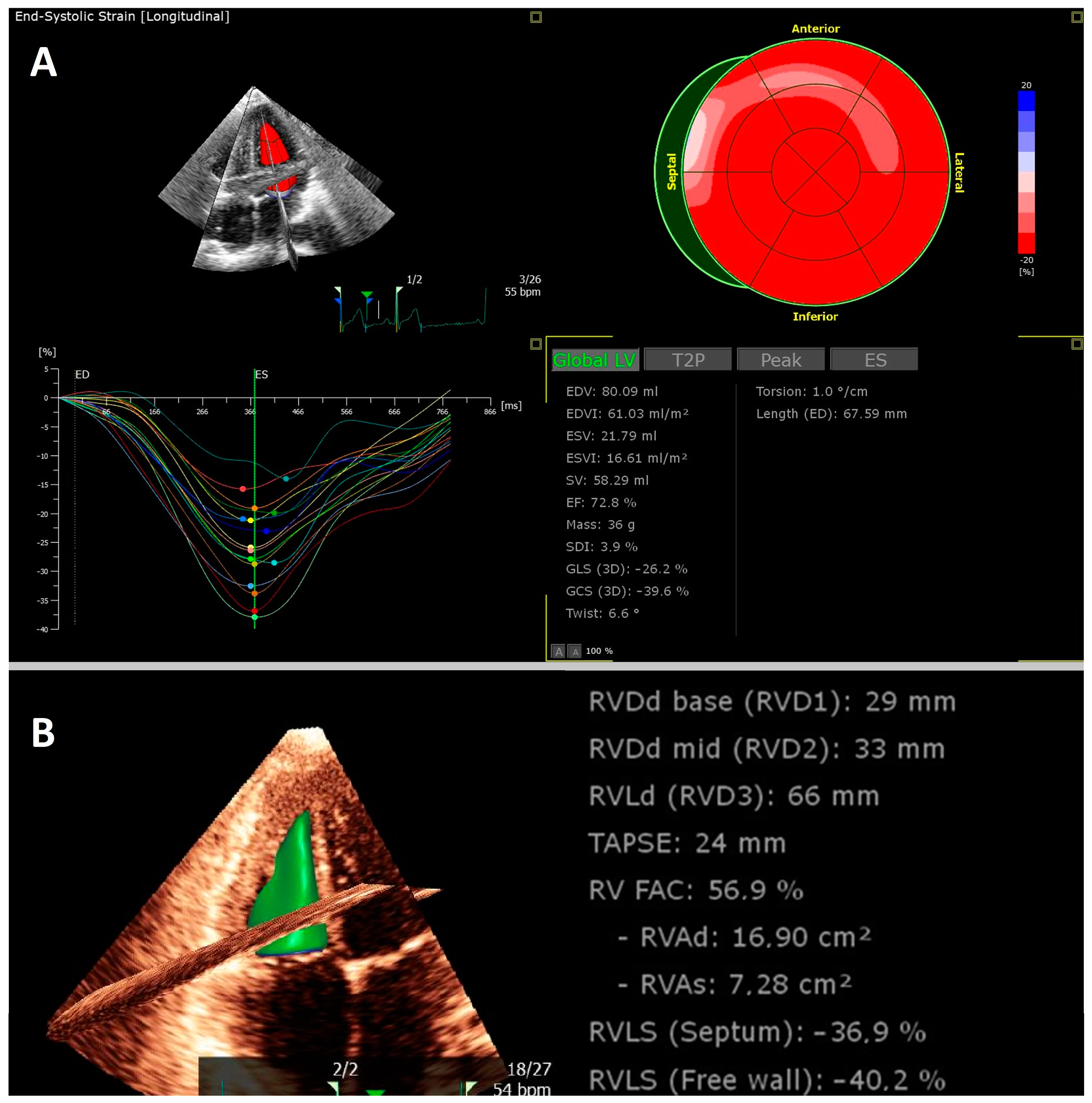
Tissue Doppler, speckling tracking and four-dimensional echocardiographic assessment of right ventricular function in children with dilated cardiomyopathy
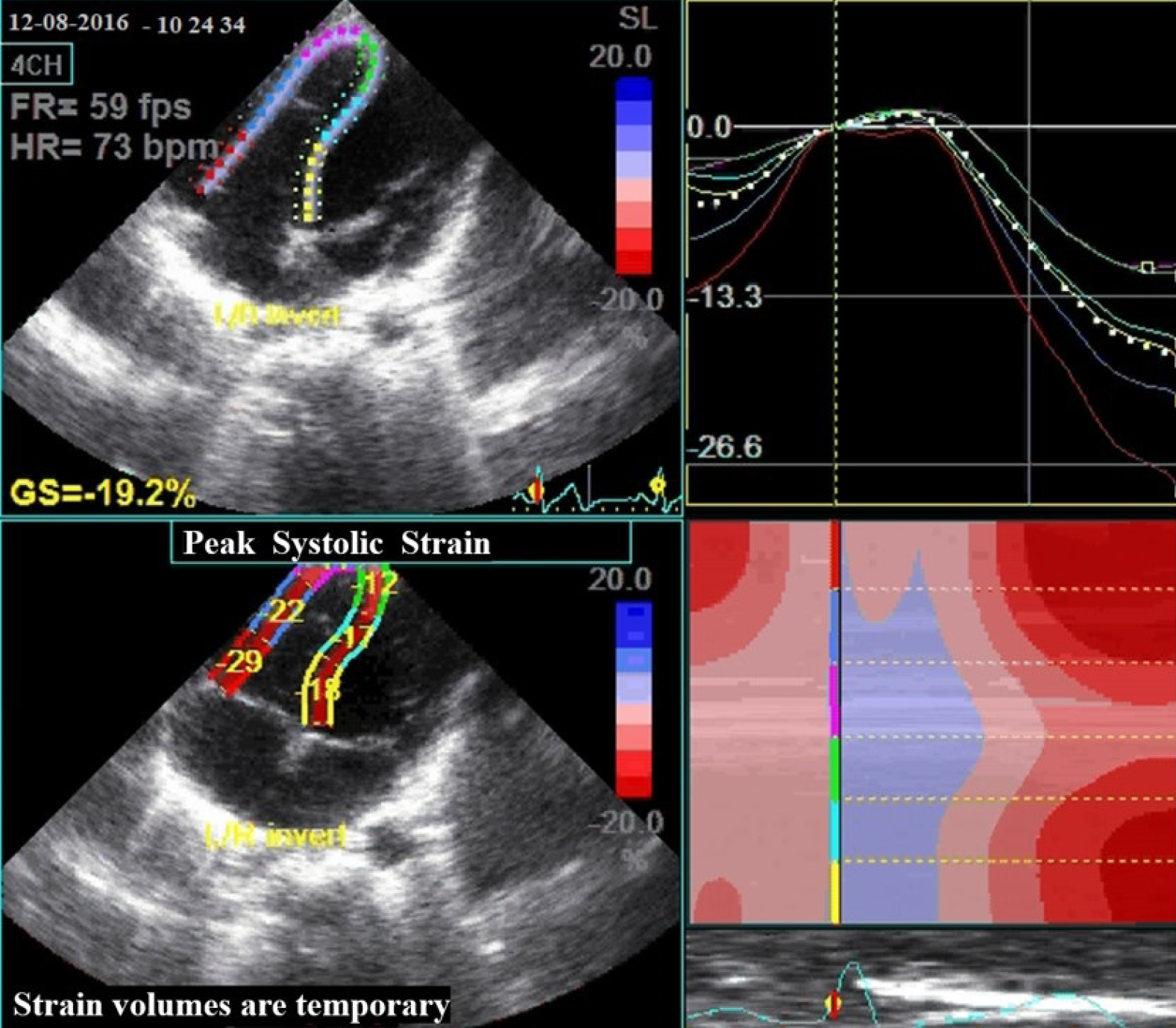
JCDD, Free Full-Text
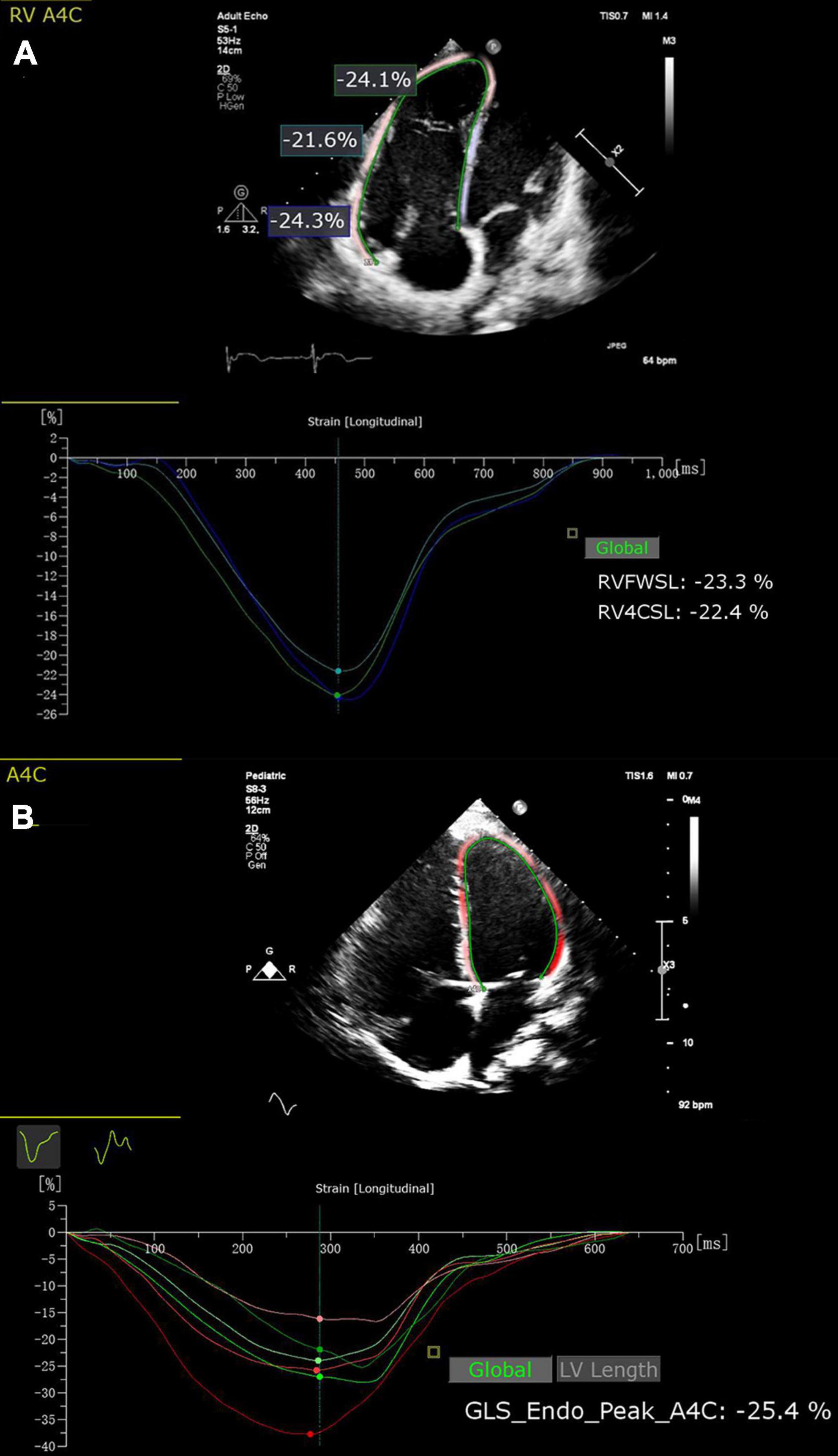
Frontiers Superior prognostic value of right ventricular free wall compared to global longitudinal strain in patients with repaired tetralogy of Fallot

Research to Practice: Assessment of Left Ventricular Global Longitudinal Strain for Surveillance of Cancer Chemotherapeutic-Related Cardiac Dysfunction

Screening of Potential Cardiac Involvement in Competitive Athletes Recovering From COVID-19: An Expert Consensus Statement - ScienceDirect

Left atrial deformation analysis by speckle tracking echocardiography to predict exercise capacity after myocardial infarction
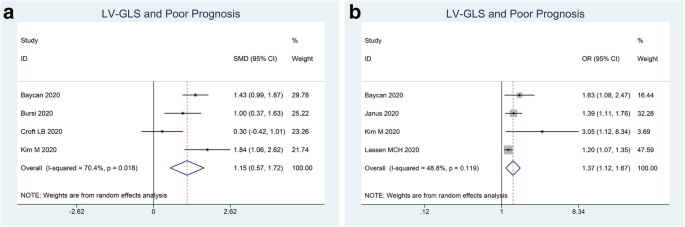
Left and right ventricular longitudinal strains are associated with poor outcome in COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Journal of Intensive Care